
Deploy a GraphQL Server with Docker and Fly
Published:
Learn how to create a GraphQL server with Node.js and Express, build an image of the server with Docker, and deploy the container to Fly.
Outline
- Introduction
- Create a GraphQL Express Server
- Create a Container Image
- Run the Docker Container and Execute a Test Query
- Publish to GitHub Container Registry
- Deploy to Fly
- Discover Related Articles
All of this project’s code can be found in the First Look monorepo on my GitHub.
Introduction
Express GraphQL is a library for building production ready GraphQL HTTP middleware. Despite the emphasis on Express in the repo name, you can create a GraphQL HTTP server with any HTTP web framework that supports connect styled middleware. This includes Connect itself, Express and Restify.
Docker is a set of tools that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in isolated packages called containers. Containers bundle their own software, libraries and configuration files. Fly is a platform for fullstack applications and databases that need to run globally. You can run arbitrary Docker containers and host popular databases like Postgres.
Create a GraphQL Express Server
This article will demonstrate how to create a Docker container with Express GraphQL.
Create Project and Install Dependencies
mkdir ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockercd ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockeryarn init -yyarn add express express-graphql graphqlCreate project files for the server, Docker image, and Docker Compose configuration.
echo > index.jsecho > Dockerfileecho > docker-compose.ymlBefore the Docker CLI sends the context to the Docker daemon, it looks for a file named .dockerignore in the root directory of the context and modifies the context to exclude files and directories that match patterns defined in the ignore file. This helps avoid sending large or sensitive files and directories to the daemon.
echo 'node_modules\nDockerfile\n.dockerignore\n.git\n.gitignore\nnpm-debug.log' > .dockerignoreInclude a .gitignore file for node_modules.
echo 'node_modules\n.DS_Store' > .gitignoreCreate graphqlHTTP Server
Enter the following code into index.js to import the graphqlHTTP function from express-graphql.
const express = require('express')const { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql')const { buildSchema } = require('graphql')
const schema = buildSchema(` type Query { hello: String }`)
const rootValue = { hello: () => 'Hello from Express GraphQL!'}
const app = express()
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({ schema, rootValue, graphiql: { headerEditorEnabled: true }, }),)
const port = process.env.PORT || 8080
app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Express GraphQL server running on http://localhost:${port}/graphql`)})graphqlHTTP accepts a wide range of options, some of the most common include:
schema- AGraphQLSchemainstance fromGraphQL.jsrootValue- A value to pass as therootValueto theexecute()functiongraphiql- If passedtrueor an options object it will present GraphiQL when the GraphQL endpoint is loaded in a browserheaderEditorEnabled- Optional boolean which enables the header editor whentrue
Run Local Server and Execute Test Query
express-graphql will accept requests with the parameters:
query- A string GraphQL document to be executedvariables- The runtime values to use for any GraphQL query variables as a JSON objectoperationName- Specifies which operation should be executed if the providedquerycontains multiple named operations
Start your server with the following command:
node indexYour terminal will log this message:
Express GraphQL server running on http://localhost:8080/graphqlOpen http://localhost:8080/graphql to see the GraphiQL explorer.
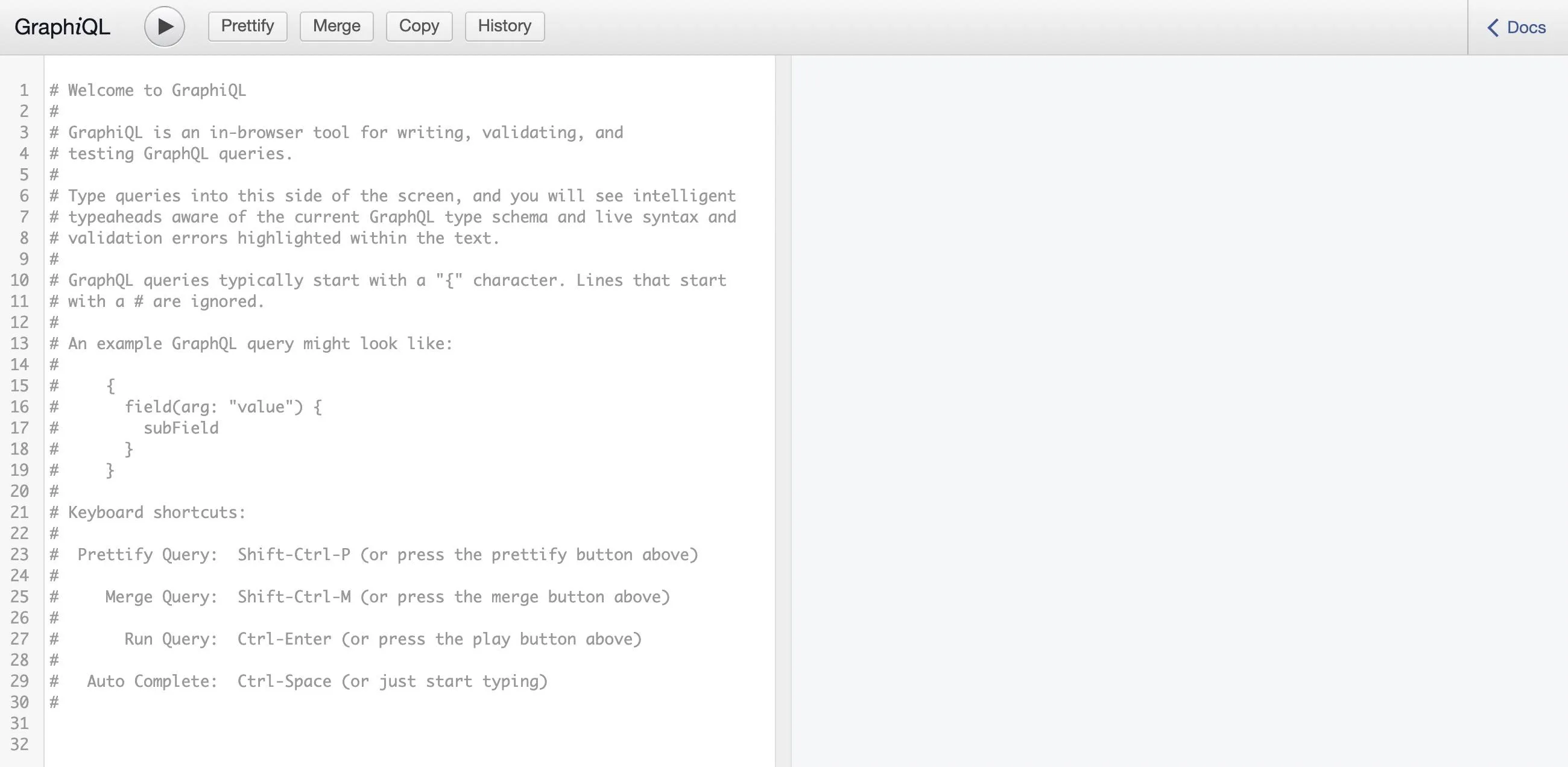
query HELLO_QUERY { hello }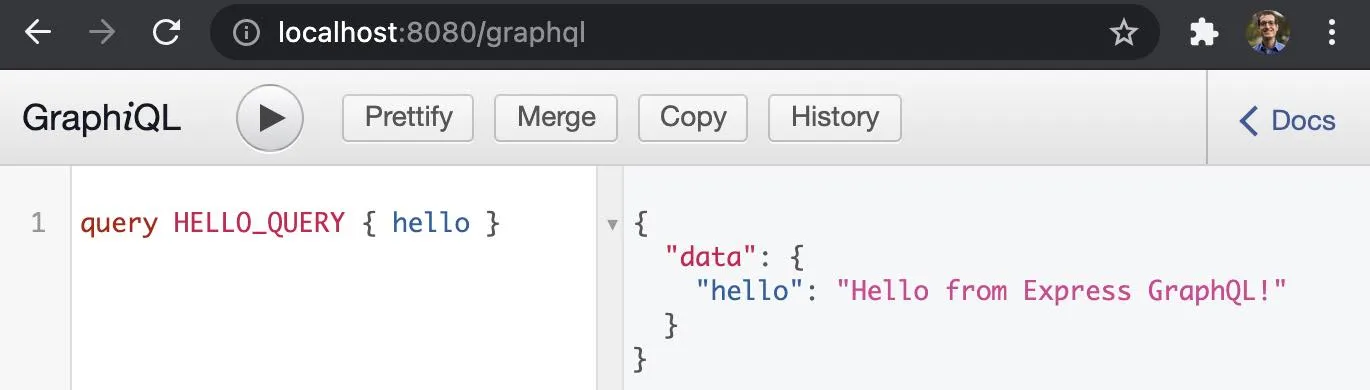
curl 'http://localhost:8080/graphql' \ --header 'content-type: application/json' \ --data '{"query":"{ hello }"}'Create a Container Image
We need to build a Docker image of your app to run this app inside a Docker container.
Dockerfile Commands
Docker can build images automatically by reading the instructions from a Dockerfile. A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble an image. Using docker build users can create an automated build that executes several command-line instructions in succession.
FROM node:14-alpineLABEL org.opencontainers.image.source https://github.com/ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockerWORKDIR /usr/src/appCOPY package*.json ./RUN yarnCOPY . ./EXPOSE 8080CMD [ "node", "index" ]Build Image and List Top Level Images
The docker build command builds an image from a Dockerfile and a “context”. A build’s context is the set of files located in the specified PATH or URL. The URL parameter can refer to three kinds of resources:
- Git repositories
- Pre-packaged tarball contexts
- Plain text files
The -t flag lets you tag your image so it’s easier to find later using the docker images command.
docker build . -t ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockerYour image will now be listed by Docker. The docker images command will list all top level images, their repository and tags, and their size.
docker imagesREPOSITORY - ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockerTAG - latestIMAGE ID - d833d418e179CREATED - About a minute agoSIZE - 122MBRun the Docker Container and Execute a Test Query
Docker runs processes in isolated containers. A container is a process which runs on a host. The host may be local or remote. When an operator executes docker run, the container process that runs is isolated in that it has its own file system, its own networking, and its own isolated process tree separate from the host.
docker run -p 49160:8080 -d ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker-d runs the container in detached mode, leaving the container running in the background. The -p flag redirects a public port to a private port inside the container.
List Containers
To test your app, get the port of your app that Docker mapped:
docker psCONTAINER ID - 4bdd108175abIMAGE - ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockerCOMMAND - "docker-entrypoint.s…"CREATED - 16 seconds agoSTATUS - Up 14 secondsPORTS - 0.0.0.0:49160->8080/tcp, :::49160->8080/tcpNAMES - silly_greiderPrint the output of your app with docker logs.
docker logs <container id>Express GraphQL server running on http://localhost:8080/graphqlDocker mapped the 8080 port inside of the container to the port 49160 on your machine. Open localhost:49160/graphql and send a hello query.
query HELLO_QUERY { hello }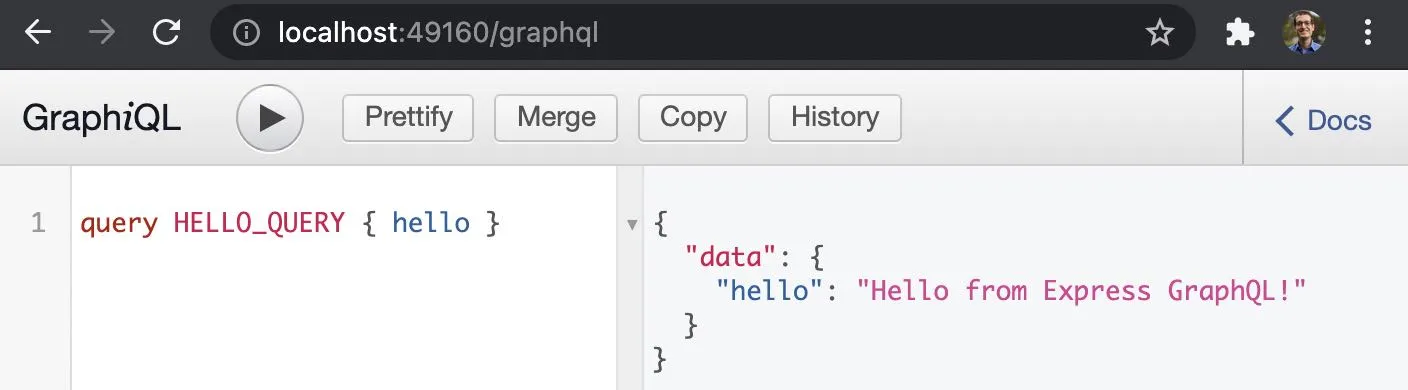
curl 'http://localhost:49160/graphql' \ --header 'content-type: application/json' \ --data '{"query":"{ hello }"}'Create a Docker Compose File
Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. After configuring your application’s services with a YAML file, you can create and start all your services with a single command. Define the services that make up your app in docker-compose.yml so they can be run together in an isolated environment.
version: "3.9"services: web: build: . ports: - "49160:8080"Stop your currently running container before running the next command or the port will be in use.
docker stop <container id>The docker compose up command aggregates the output of each container. It builds, (re)creates, starts, and attaches to containers for a service.
docker compose upPublish to GitHub Container Registry
We can publish this image to the GitHub Container Registry with GitHub Packages. This will require pushing our project to a GitHub repository.
Create GitHub Repo and Login to Container Registry
Initialize Git, create a blank repository, and push to newly created repo
git initgit add .git commit -m "A container for my graph"gh repo create ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker --public \ --push \ --source=. \ --description="An example GraphQL Express server containerized with Docker and deployed on Fly" \ --remote=upstreamGitHub Packages is a platform for hosting and managing packages that combines your source code and packages in one place including containers and other dependencies.
- You can integrate GitHub Packages with GitHub APIs, GitHub Actions, and webhooks to create an end-to-end DevOps workflow that includes your code, CI, and deployment solutions.
- GitHub Packages offers different package registries for commonly used package managers, such as npm, RubyGems, Maven, Gradle, and Docker.
- GitHub’s Container registry is optimized for containers and supports Docker and OCI images.
To login to the GitHub Container Registry, create a PAT (personal access token) with the ability to read, write, and delete packages and include it instead of xxxx.
export CR_PAT=xxxxLogin with your own username in place of ajcwebdev.
echo $CR_PAT | docker login ghcr.io -u ajcwebdev --password-stdinTag Image, Push to Registry, and Pull Image
Tag image with the docker tag command.
docker tag ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker ghcr.io/ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockerPush to the registry with the docker push command.
docker push ghcr.io/ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker:latestTo test that our project has a docker image published to a public registry, pull it from your local development environment with the docker pull command.
docker pull ghcr.io/ajcwebdev/ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockerYou can view this published container on my GitHub.
Deploy to Fly
You can download the flyctl CLI on Mac, Linux, or Windows.
brew install superfly/tap/flyctlInstall and Authenticate Fly CLI
If you are a new user you can create an account with fly auth signup.
fly auth signupYou will also be prompted for credit card payment information, required for charges outside the free plan on Fly. See Pricing for more details. If you already have an account you can login with fly auth login.
fly auth loginLaunch and Deploy Fly App
Run fly launch in the directory with your source code to configure your app for deployment. This will create and configure a fly app by inspecting your source code and prompting you to deploy.
fly launch --name ajcwebdev-express-graphql-dockerSelect a region and skip adding a PostgreSQL database. When asked if you want to deploy, select No.
Your app is ready. Deploy with `flyctl deploy`? Would you like to deploy now? NoThe launch command created a fly.toml file.
app = "ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker"
kill_signal = "SIGINT"kill_timeout = 5processes = []
[env]
[experimental] allowed_public_ports = [] auto_rollback = true
[[services]] http_checks = [] internal_port = 8080 processes = ["app"] protocol = "tcp" script_checks = []
[services.concurrency] hard_limit = 25 soft_limit = 20 type = "connections"
[[services.ports]] handlers = ["http"] port = 80
[[services.ports]] handlers = ["tls", "http"] port = 443
[[services.tcp_checks]] grace_period = "1s" interval = "15s" restart_limit = 6 timeout = "2s"Add the following PORT number under env.
[env] PORT = 8080Run the fly deploy command to deploy your launched app.
fly deployShow the Application Status
Status includes application details, tasks, most recent deployment details and in which regions it is currently allocated.
fly statusApp Name = ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker Owner = personal Version = 0 Status = running Hostname = ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker.fly.dev
Deployment Status ID = fd7bf249-c37f-7b16-5643-9bfd104a2077 Version = v0 Status = successful Description = Deployment completed successfully Instances = 1 desired, 1 placed, 1 healthy, 0 unhealthy
InstancesID TASK VERSION REGION DESIRED STATUS HEALTH CHECKS RESTARTS CREATED9eb4eaf9 app 0 sjc run running 1 total, 1 passing 0 1m15s agoVisit ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker.fly.dev/graphql to see the site and run a test query.
query HELLO_QUERY { hello }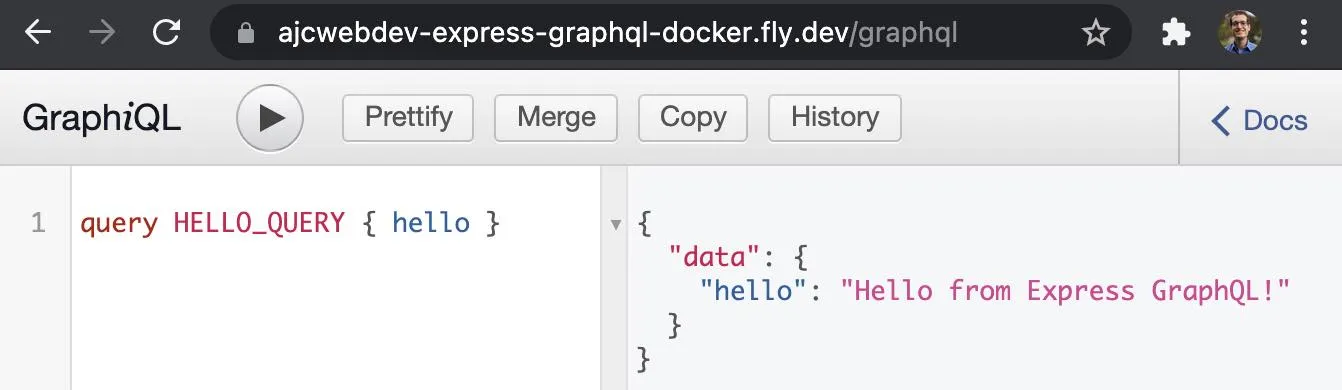
curl 'https://ajcwebdev-express-graphql-docker.fly.dev/graphql' \ --header 'content-type: application/json' \ --data '{"query":"{ hello }"}'