
A First Look at Serverless Cloud
Serverless Cloud is a new serverless app platform from Serverless, Inc. Unlike the Serverless Framework, it lives on a new hosting service in the cloud.
- Introduction
- Setup
- Index Entry File
- Sample Todos
- Tests
- Static Assets
- Modify HTML Index File and Deploy to Production
- Dashboard
- Summary
All of this project's code can be found in the First Look monorepo on my GitHub.
Introduction
NOTE: Serverless Cloud no longer exists in the form documented in this tutorial. It has been rebranded to Ampt. One day I may update this blog post, but if you're reading this now you should not attempt to run any of this code expecting it to work.
Serverless Cloud is a new serverless app platform from Serverless, Inc. Unlike the company's initial product, the Serverless Framework, it does not deploy your application directly to AWS. Instead, your apps are instantly deployed and live on a new hosting service in the cloud with a dashboard and real-time logs.
Setup
Install Cloud CLI
Install @serverless/cloud from npm.
npm i -g @serverless/cloudInitialize Service
Create a blank folder on your local machine for your service's code and initialize your Serverless Cloud service with the cloud command.
mkdir ajcwebdev-serverless-cloud
cd ajcwebdev-serverless-cloud
cloudYour browser will open automatically and log you in via the CLI or provide a login link in the terminal. Once you are connected you will be given an activation code to enter when prompted.
Deploy to Staging Environment
Give you service a name and deploy it with deploy dev in the interactive terminal.
deploy devYou can also use cloud deploy dev if you want to clone one of these projects from a repo and immediately deploy it.
cloud deploy devYou will be given a deployed endpoint (fabulous-mvp-00zr8.cloud.serverless.com in my case) with a sample todo app.
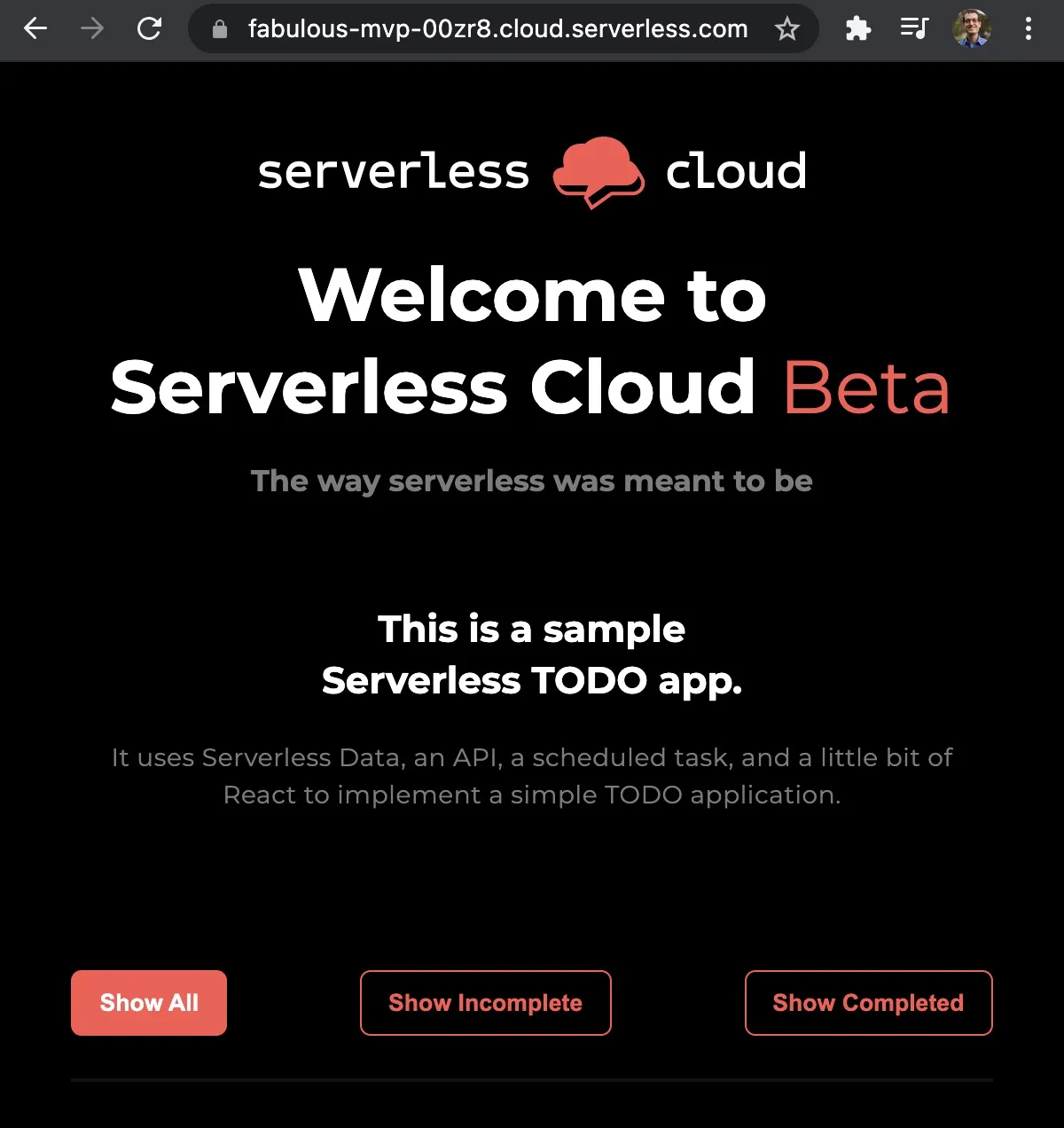
Add a few todos.
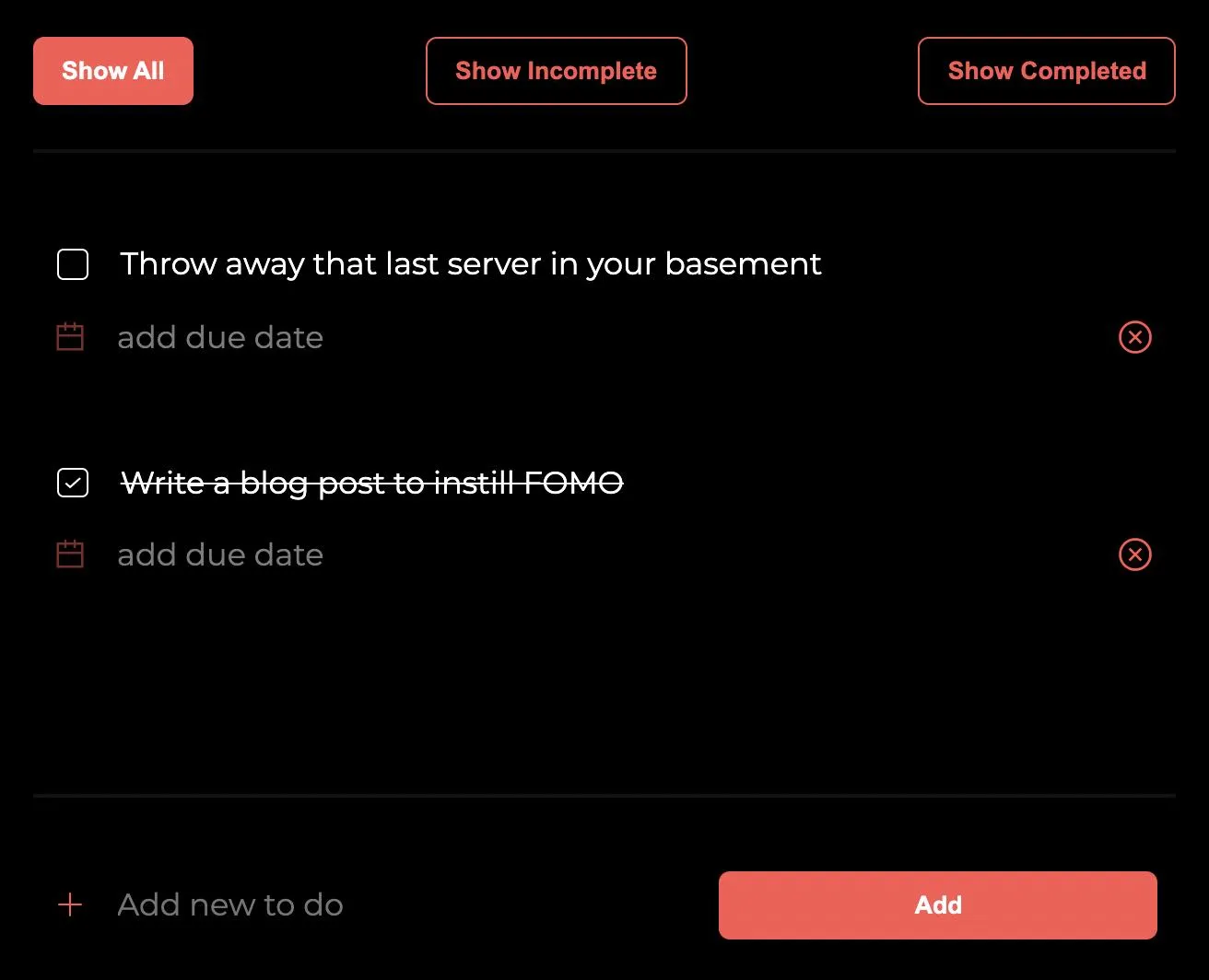
The @serverless/cloud package is included by default in the cloud runtime, so it does not need to be included as a dependency in package.json.
{
"name": "ajcwebdev-serverless-cloud",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Serverless Cloud todo api",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"start": "cloud",
"test": "cloud test"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@jest/globals": "^27.1.0",
"@serverless/cloud": "^0.0.22"
},
"serverless": {
"org": "ajcwebdev",
"service": "ajcwebdev-serverless-cloud"
}
}Index Entry File
We import a handful of modules from @serverless/cloud at the top of our index.js file.
// index.js
import {
api, data, schedule, params
} from '@serverless/cloud'
api.get('/todos', async (req, res) => {...})
api.post('/todos/:id', async (req, res) => {...})
api.delete('/todos/:id', async (req, res) => {...})
api.use((err, req, res, next) => {...})
schedule.every("60 minutes", async () => {...})
const getTodos = async (status, meta) => {...}apiis used to build REST APIs.api.get-GETmethodapi.post-POSTmethodapi.delete-DELETEmethodapi.use- Middleware
datais used to access Serverless Data.data.get- Reads the datadata.getByLabel- Reads the data with a specified labeldata.set- Writes the data to storagedata.remove- Deletes the data
scheduleis used to create scheduled tasks.schedule.every- Runs on a specified interval of time such as every 60 minutes
getTodos Function
This function can be reused in different API paths to get all the todos or to get a specific todo based on its label.
// index.js
const getTodos = async (status, meta) => {
let result
if (status === 'all') {
result = await data.get('todo:*', meta)
} else if (status === 'complete') {
result = await data.getByLabel('label1','complete:*', meta)
} else {
result = await data.getByLabel('label1','incomplete:*', meta)
}
return {
items: result.items.map(
item => item.value
)
}
}GET Todos
This function calls our getTodos function with the status and returns the results.
// index.js
api.get('/todos', async (req, res) => {
let result = await getTodos(
req.query.status,
req.query.meta ? true : {}
)
console.log(params.CLOUD_URL)
res.send({
items: result.items
})
})POST Updates to a Todo
This function takes the body of the request and sets it to data. The body can include a duedate. It also includes an id, createdAt date, and status that can be complete or incomplete. After setting the todo, the getTodos query is run again on all the todos and the updated list is returned.
// index.js
api.post('/todos/:id', async (req, res) => {
console.log(new Date().toISOString())
let body = req.body
if (body.duedate) {
body.duedate = new Date(body.duedate).toISOString()
}
await data.set(
`todo:${req.params.id}`,
{
...body,
createdAt: Date.now()
},
Object.assign({},
req.body.status ?
{
label1: body.status === 'complete'
? `complete:${new Date().toISOString()}`
: `incomplete:${body.duedate ? body.duedate : '9999' }` }
: null
)
)
let result = await getTodos(
req.query.status
)
res.send({
items: result.items
})
})Pay no attention to the ternary soup in Object.assign if it doesn't make any sense. Just try to leave it alone and don't touch it.
DELETE a Todo
This function deletes the todo with data.remove and then queries and returns the remaining todos in the list.
// index.js
api.delete('/todos/:id', async (req, res) => {
await data.remove(`todo:${req.params.id}`)
let result = await getTodos(req.query.status)
res.send({
items: result.items
})
})Custom Error Handler Middleware
This function provides middleware for error handling. Errors are also streamed live to your terminal in dev mode.
// index.js
api.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err.stack)
if (!err.statusCode) {
err.statusCode = 500
}
const error = {
name: err.name,
statusCode: err.statusCode,
message: err.message,
}
res.status(err.statusCode).json(error)
})Check for Overdue Todos Hourly
Sometimes you might want to run code on a schedule, like if you want to send alerts when items are overdue. This function looks for items that are overdue, loops through the overdue items, and sends an alert if necessary.
// index.js
schedule.every("60 minutes", async () => {
console.log(`Checking for overdue TODOs...`)
let overdueItems = await data.getByLabel(
'label1',
`incomplete:<${new Date().toISOString()}`
)
if (overdueItems.items.length === 0) {
console.log(`Nothing overdue!`)
}
for (let item of overdueItems.items) {
console.log(
`ALERT: '${item.value.name}' is overdue!!!`
)
}
})Sample Todos
Open data.json to see sample todos.
{
"key": "todo:1",
"value": {
"id": "1",
"name": "Deploy an amazing Serverless Cloud app",
"status": "complete",
"completed": "2021-07-01T12:00:00.000Z",
"createdAt": 1627316142196
},
"label1": "complete:2021-07-01T012:00:00.000Z"
},Tests
There are tests. One day I'll write a test, I promise.
Static Assets
You can serve up static assets from the static folder. The folder currently contains:
assetsfolder for imagesindex.htmlto serve the main pagestyles.cssfor stylingtodos.jsfor all the React code so you can scare the backend developers on your team
Modify HTML Index File and Deploy to Production
Change the <header> in index.html.
<header>
<div>
<h1 class="text-center">
ajcwebdev serverless cloud
</h1>
<h3 class="grey text-center">
Seriously, there are so few servers you wouldn't believe it
</h3>
</div>
</header>Deploy to production with cloud deploy prod or deploy prod in the interactive terminal session.
cloud deploy prodThe link (novel-app-fpp5w.cloud.serverless.com) will be automatically pasted to your clipboard cause having to copy links is for noobs.
Dashboard
Since this is a cloud that means it has to have a dashboard, right? How else can I perform my ClickOps duties?
Services
Serverless Cloud allows you to build services within your team's organization.
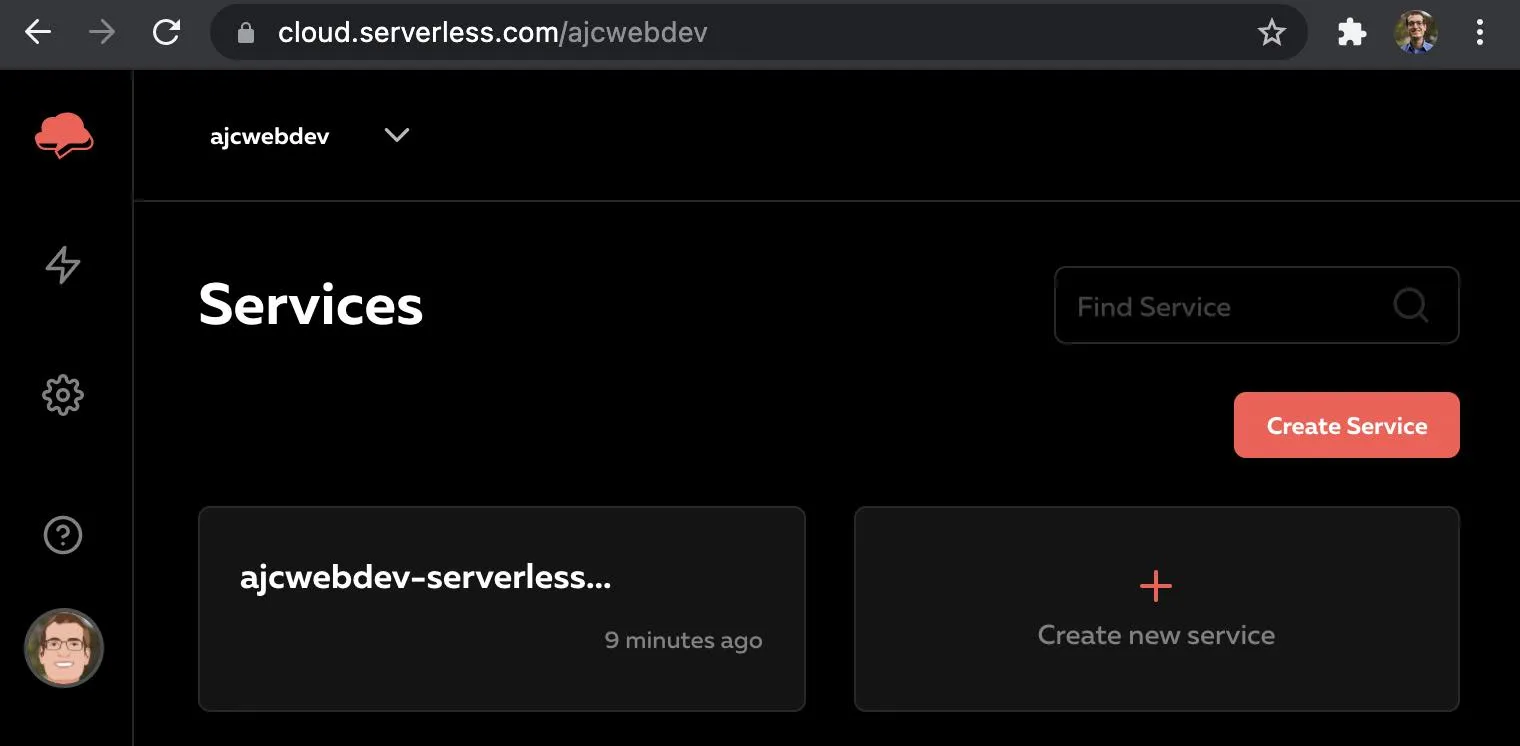
You can create as many services as you want for different use cases or applications.
Instances
Each instance is completely separate from all the other instances in a service and store their own copy of the data.
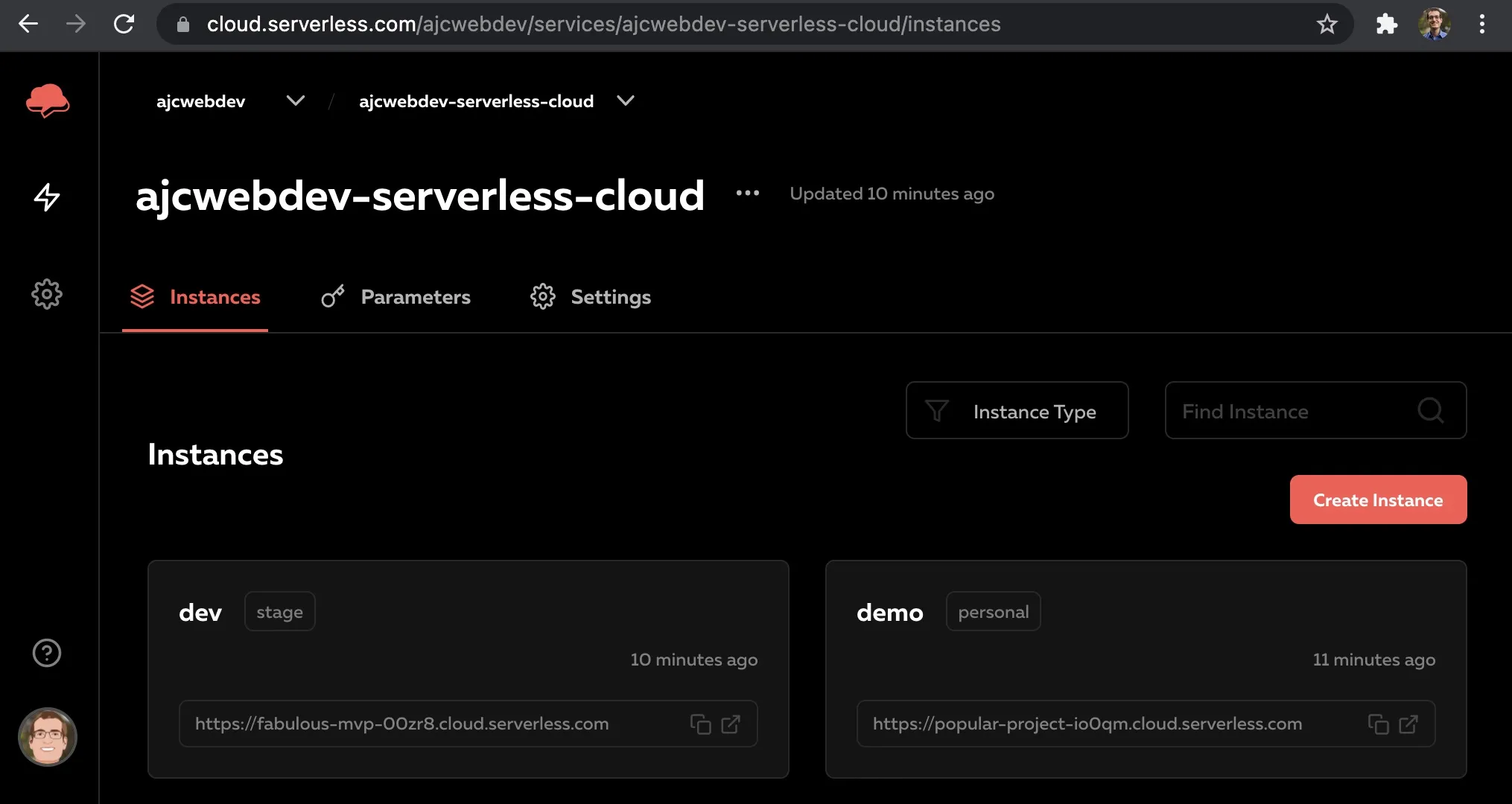
The environments within instances are identical, so you can ensure that your application will behave exactly the same across all of them.
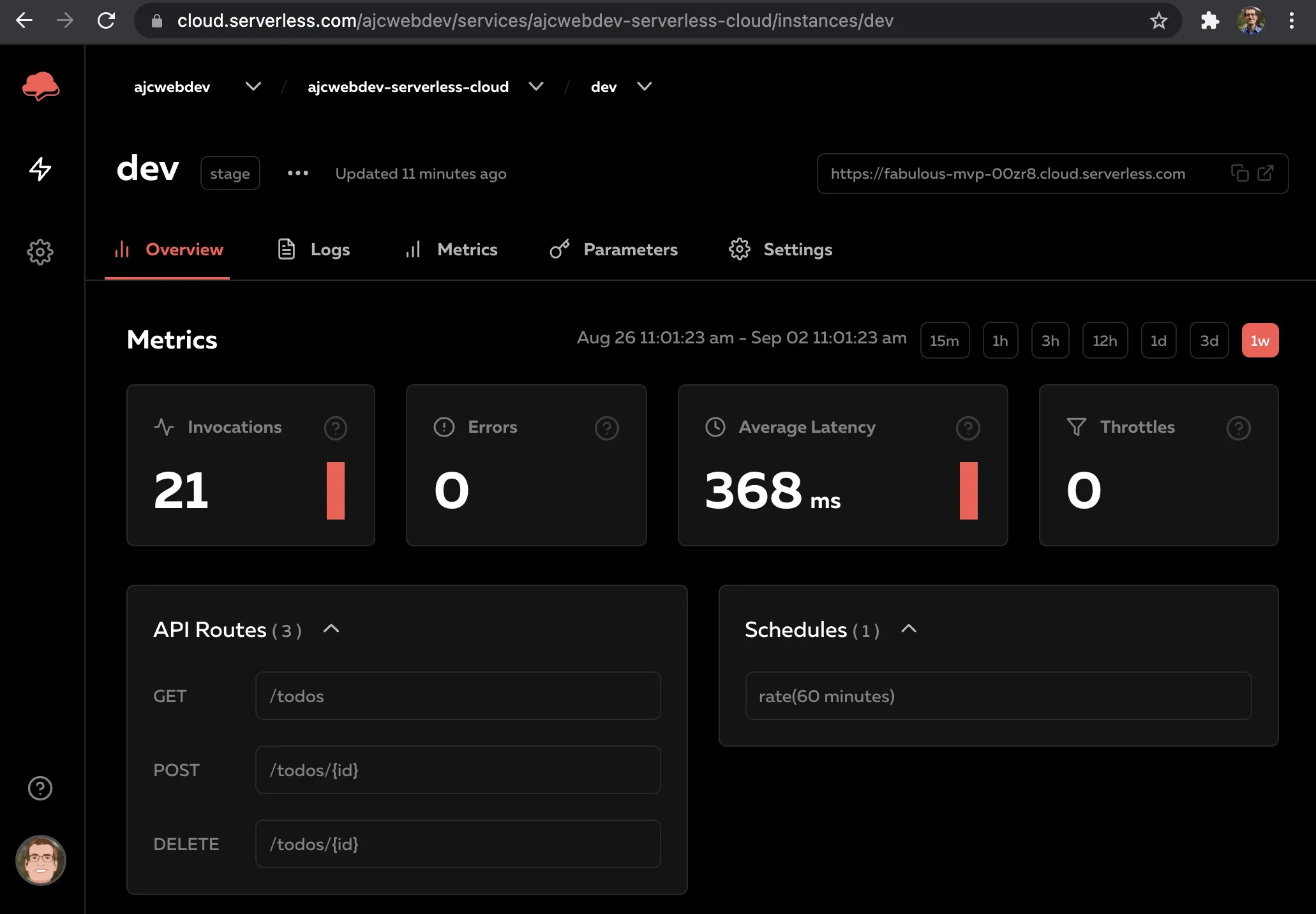
Metrics
Numbers that tell you information about stuff.
Summary
Pretty cool. Nothing blew up, it worked as expected, and I had a deployed application in under 10 seconds.